What Is Genetic Counseling?
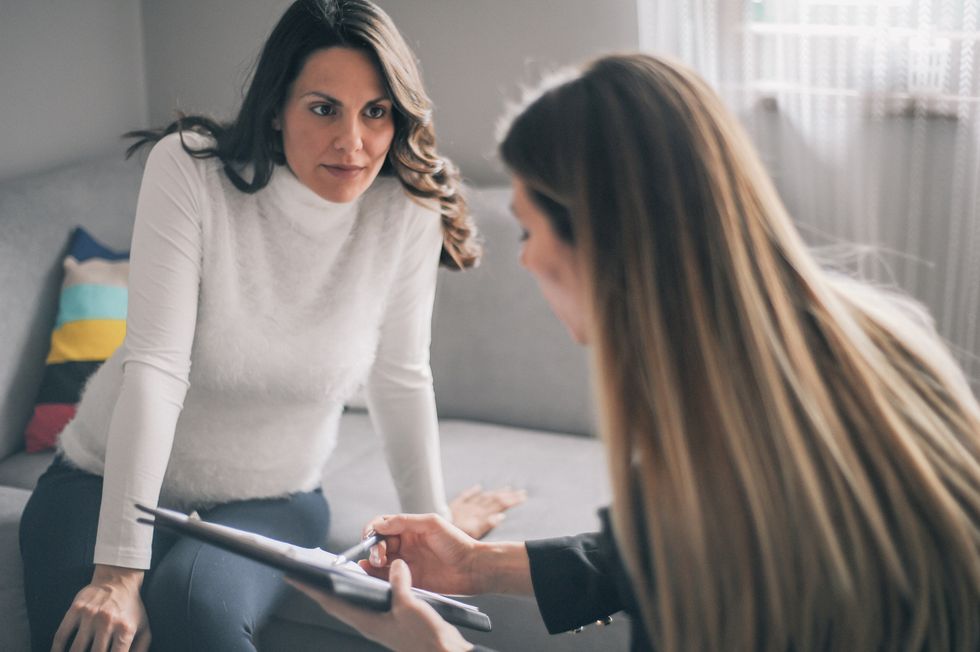
When we hear the word, "counselor," genetics probably isn't the first thing that comes to mind. But in addition to marriage counselors and camp counselors, there is a whole field of genetic counselors who help people navigate the complicated world of inherited disease. The nature of genetic testing is complex, with implications for both the person being tested and his or her family. Based on personal and family history, genetic counselors help individuals decide whether to undergo genetic testing, and they assist those who do decide to go through testing through the process of digesting the results. Genetic counseling is an important part of the genetic testing process.
What is a Genetic Counselor?
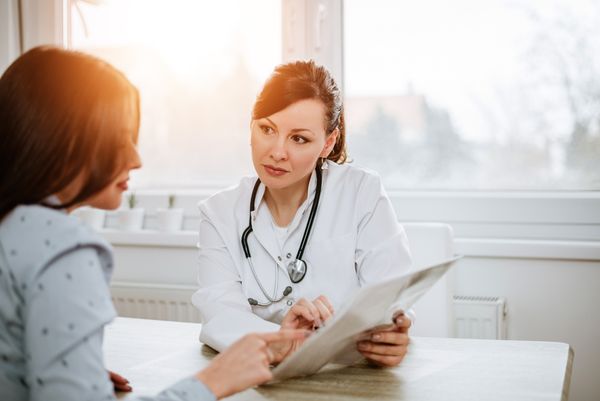
A genetic counselor is a health care professional who specializes in counseling, human genetics, and genetic testing. He or she reviews your family and medical histories to determine if there appears to be a hereditary pattern of disease.
What Can I Expect From a Genetic Counseling Session?
A genetic counseling session can last any amount of time, depending upon the situation. Unlike most medical appointments, a counseling session may be a family affair and include all concerned relatives.
Genetic counseling typically includes:
- gathering background medical information about you and your family
- risk assessment for having a genetic disease or mutation
- discussion about genes that may be appropriate for testing, if indicated
- discussion about the risks, benefits and limitations of testing
- providing information on inheritance, the genetic testing procedure, the possible results and what they mean
- informed consent, if genetic testing is indicated and you elect to have it
Genetic counseling helps provide the education necessary to make an informed decision regarding further genetic testing and/or disease prevention or treatment. Genetic counselors are trained to assist you in the decision-making process. Whether you choose to include genetic testing in this process is up to you.
Because family history is so crucial in assessing for a genetic condition and determining which genes to consider testing, a counselor may request medical records to confirm a diagnosis, especially if you're trying to determine whether a family pattern of cancer or another condition is hereditary.
These medical records are important because family member recollections can be inaccurate—relatives may misremember who had which disease or even what type of disease. And many conditions were either not discussed or not diagnosed in the past. With multiple family members at a session, a genetic counselor can get a complete family account and help tease out details to better identify potential patterns.
Privacy Concerns in Genetic Counseling
Genetic counselors are committed to protecting the privacy of their patients. They will not contact other family members without your permission, though they may encourage you to share results that might affect your relatives' health. The Genetic Information Nondiscrimination Act of 2008 (GINA) is a new federal law that specifically addresses genetic discrimination with regard to health insurance and employment. The law took effect in 2009.
How to Find a Genetic Counselor
You can find a genetic counselor at https://www.nsgc.org, the Web site for the National Society of Genetic Counselors. The core credentials are a master's degree in the field and certification conferring the designation of certified genetic counselor (CGC).
- Family History and Breast Cancer Screening ›
- Fast Facts: What You Need to Know About Genetics and Breast Cancer Risk ›
- What’s in an At-Home DNA Test? ›
- How Do Genes Affect Your Health? ›
- Genetic Testing ›