What is atopic dermatitis?
Atopic dermatitis (AD) is the most common type of eczema and can affect any part of the body.
Different body zones should get different types of care.
Did you know?
AD causes inflammation inside and outside the body. Even when skin is clear, the inflammation is still under your skin.
Symptoms of AD
Hives (red, swollen, itchy bumps)
Rashes
Burning or itchy skin
Broken skin caused from scratching or dry skin
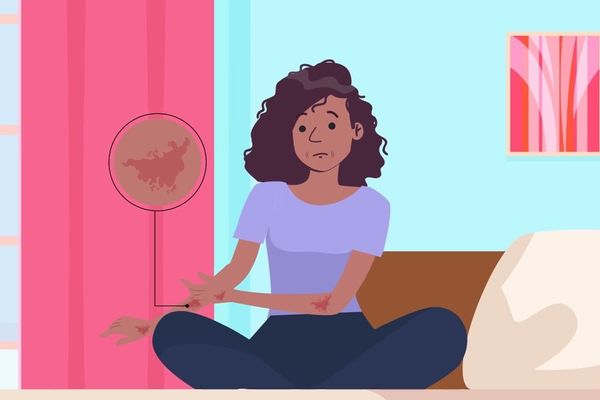
Identifying AD
Eczema looks different on different skin types and tones and sometimes can be mistaken for dry skin.
Be sure to tell your healthcare provider about any pain, itchiness, irritation or skin changes and any products that might be affecting your skin.
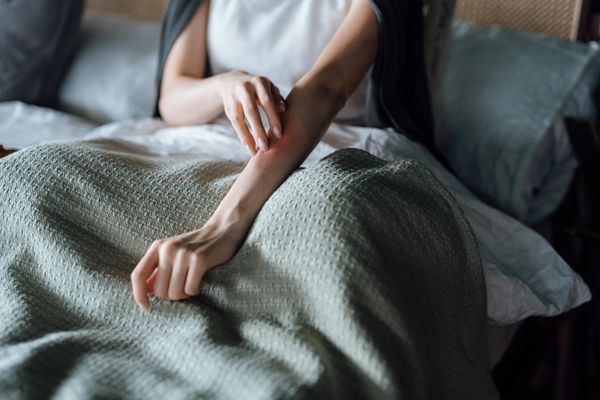
Itch-Scratch-Itch
The “itch-scratch cycle” is when itching leads to scratching, which leads to more inflammation, which leads to more itching.
Tip:
Fragrances, dyes or alcohols are common triggers for AD. Try to avoid them in your everyday products and clothing.
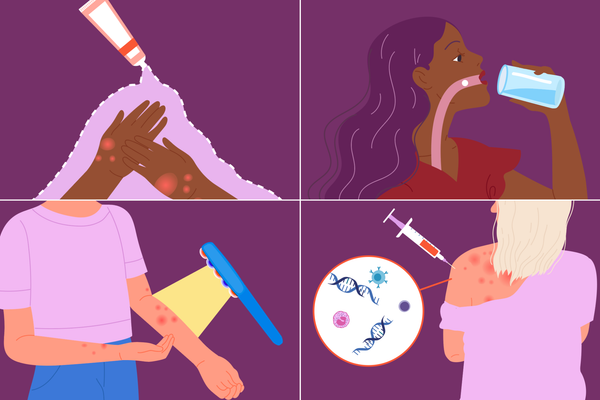
Treatment options
There’s no cure for eczema, but learning triggers and finding treatment options that work for you can help.
General treatment options include:
- Creams and ointments
- Biologic medication
- Oral or injectable corticosteroids
- Topical antibiotics
- Light therapy
- Antihistamines
- Fragrance-free moisturizers
- Lukewarm baths with or without oatmeal, oils or baking soda
- Bandages and wet wraps
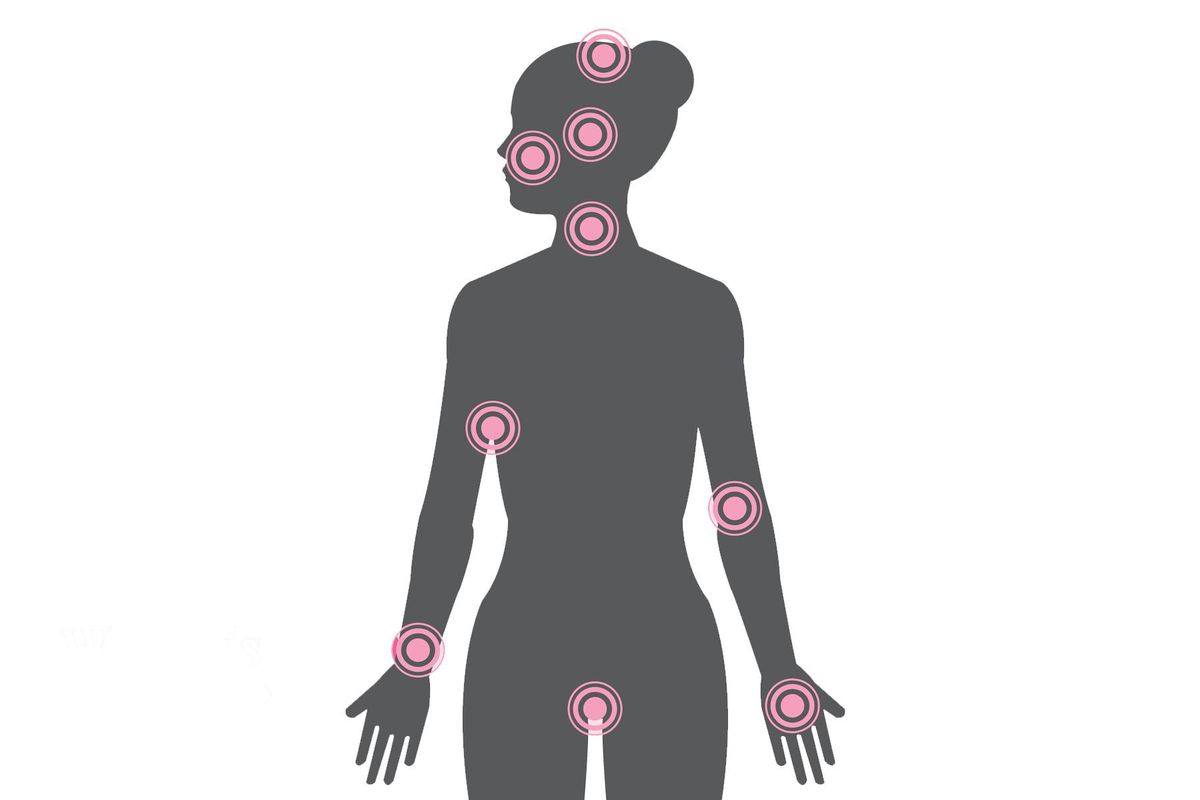
Where is your AD?
The location of your AD can change your treatment options.
Body zone | Treatment options |
Scalp |
|
Eyelids, armpits, mouth and groin |
|
Face, mouth and neck |
|
Elbows, ears, knees, wrists, ankles, hands and feet |
|
Vagina (vulvar dermatoses) |
|
This resource was created with support from Regeneron and Sanofi Genzyme.
- What It's Like to Care for a Child With Severe Eczema - HealthyWomen ›
- Atopic Dermatitis Shows Up on Your Skin, but Its Effects Go Much ... ›
- Clinically Speaking: Questions to Ask Your Healthcare Provider ... ›
- Living With Atopic Dermatitis (AD) - HealthyWomen ›
- Coping With Atopic Dermatitis - HealthyWomen ›
- Type 2 Inflammation May Be Contributing to Your Atopic Dermatitis - HealthyWomen ›
- Options for Treating Atopic Dermatitis - HealthyWomen ›
- WomenTalk: Flare and Care for Eczema - HealthyWomen ›