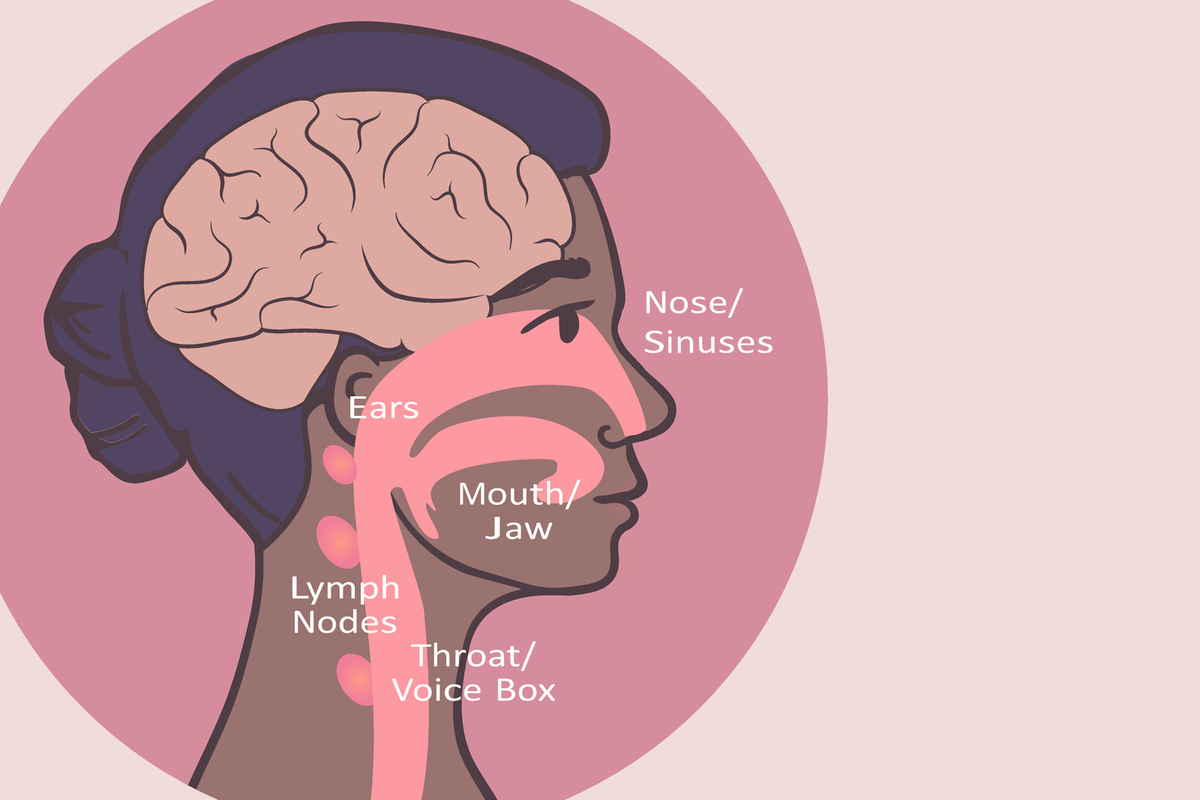
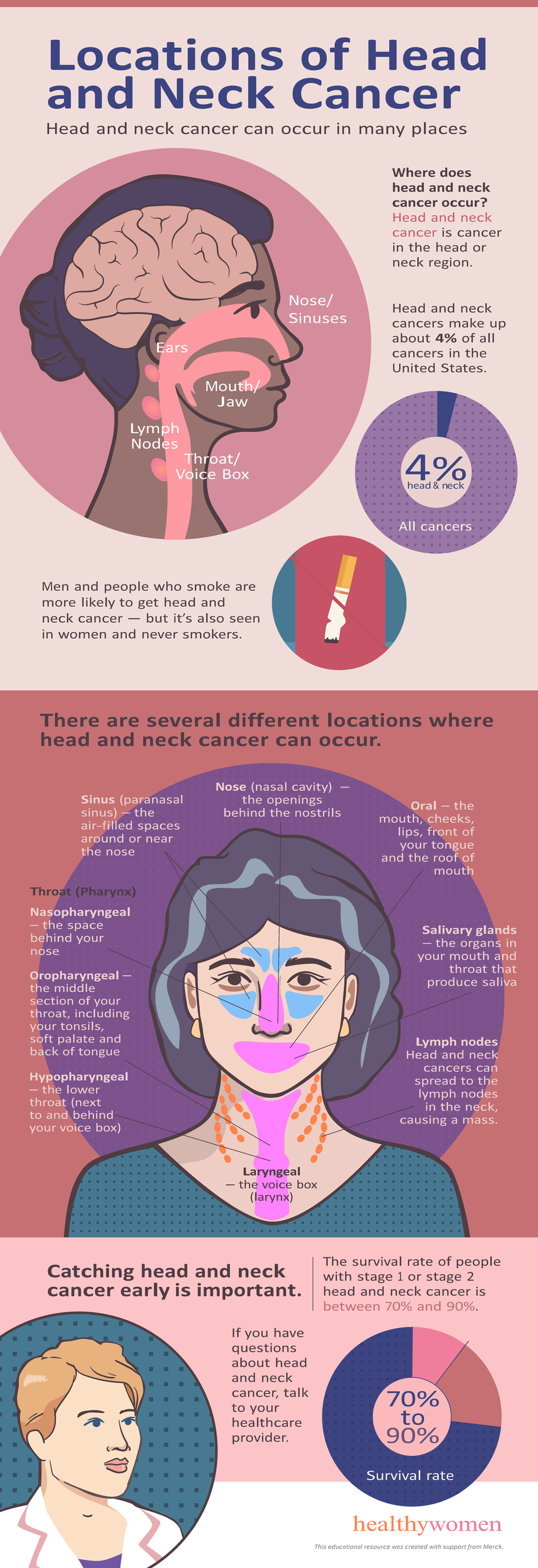
Where does head and neck cancer occur?
Head and neck cancer is cancer in the head or neck region.
Head and neck cancers make up about 4% of all cancers in the United States.
Men are more likely to get head and neck cancer, but it’s also seen in women and never smokers.
There are several different locations where head and neck cancer can occur.
Voice Box (Larynx)
Laryngeal cancer = the voice box (larynx)
Throat (Pharynx)
Hypopharyngeal cancer = the lower throat (next to and behind your voice box)
Oropharyngeal cancer = the middle section of your throat, including your tonsils, soft palate and back of tongue
Nasopharyngeal cancer = the space behind your nose
Mouth
Oral cancer = the mouth, cheeks, lips, front of your tongue and the roof of mouth
Nose and sinuses
Nose (nasal cavity) = the openings behind the nostrils
Sinus (paranasal sinus) cancer = the air-filled spaces around or near the nose
Salivary glands
Salivary gland cancer = the salivary glands, the organs in your mouth and throat that produce saliva
Neck
Head and neck cancers can spread to the lymph nodes in the neck, causing a mass.
Catching head and neck cancer early is important. The survival rate of people with stage 1 or stage 2 head and neck cancer is between 70% and 90% .
If you have questions about head and neck cancer, talk to your healthcare provider.
This educational resource was created with support from Merck.
- Clinically Speaking: Questions to Ask Your Healthcare Provider About Head and Neck Cancer ›
- Coping With the Emotional Impact of Head and Neck Cancer ›
- Fast Facts: What You Need to Know About Head and Neck Cancer ›
- Understanding Head and Neck Cancer ›
- 7 Ways to Reduce the Risk of Head and Neck Cancers ›
- What Is the Link Between HPV & Head and Neck Cancers? - HealthyWomen ›
- True or False: Head and Neck Cancers ›
- Verdadero o falso: Cánceres de cabeza y cuello - HealthyWomen ›
- 9 Signs You Might Have Head and Neck Cancer - HealthyWomen ›
- Síntomas de cáncer de cabeza y cuello - HealthyWomen ›